Food tourism is an important carrier to meet the new needs of the people for a better life, and it is also a new driving force to promote the high-quality development of the tourism industry. In order to promote the deep integration and development of "food tourism" in China, and actively explore the development path and market cultivation methods of food tourism resources, on September 16, 2023, the "2023 China Food Tourism Development Forum" jointly hosted by the China Tourism Research Institute, the Hunan Provincial Department of Culture and Tourism, and the People's Government of Chenzhou City, Hunan Province, was opened in Chenzhou City, Hunan Province. Dean Dai Bin delivered a keynote speech titled "New Driving Force of Food Tourism, High Quality Tourism -2023 China Food Tourism Development Report" around the theme of food tourism. The full text is shared as follows:
The great affairs of the country can only be achieved through worship and military service. Whether it's the solemn sacrifice of pursuing the distant future or the war to protect the country and the people, food and drink are indispensable. As the saying goes, food and forage come first before the troops move. However, with the evolution of civilization, such obvious facts have gradually and unconsciously been obscured by certain metaphysical concepts. In the field of tourism, we are fascinated by the distant scenery and past, and climb steep paths at the county, provincial, municipal, national, and world-class levels. We study the sky and earth for city slogans that are not surprising, and write lengthy articles on concepts such as authenticity, gaze, and pleasure. However, few people pay attention to the decisive role of catering in tourism. This report pays tribute to Engels' brilliant document "Speech at Marx's Tomb" published on March 22, 1883, which stated that "people must first eat, drink, live, and dress before engaging in politics, science, art, religion, and so on... People's state facilities, legal views, art, and even religious concepts are developed on this basis, and therefore must also be explained by this basis, rather than doing the opposite as in the past.
1、 Catering is a fundamental element of mass tourism, and cuisine is a rigid demand for moderately prosperous tourism
Tourism is a long-standing way of life for humanity and a fundamental right of citizens. But this way of life and basic rights did not fall from the sky, but awakened and consciously after solving basic living needs such as food, clothing, and housing. Whether it is a long journey or a short-term stay at a destination, tourism requires first solving the problems of food and accommodation before sightseeing, sightseeing, leisure, and shopping. In most cases, they can accept or even pursue different scenery, customs, and culture, but cannot always accept ingredients and cooking methods that are different from their usual living environment. If hotels, buses, and tour guides have put a "tourism shield" on the destination, then childhood dietary habits have built a "cultural wall" for tourists to integrate into local life. Whether it is the requirement for star rated hotels to provide Western cuisine to welcome inbound tourists in the 1980s, or the use of hotel coffee pots to cook instant noodles by outbound tourists twenty years ago, both are the result of the objective existence of the "tourism cover" and "cultural wall". With the improvement of people's living standards, especially the enrichment of cross regional, cross international, and intercontinental travel experience, tourists gradually accept a rich and colorful catering culture, and further actively pursue exotic cuisine, ultimately making food an increasingly important component of the tourism attraction system. This is also the inherent driving force and evolutionary mechanism of the shift from tourism catering to food tourism. It is precisely because of the existence of catering and cuisine that true international tourist destinations and world-class tourist cities always walk between differences and similarities, that is, they cannot only provide tourists with undifferentiated fast food, nor can they promote "dark cuisine" without taking it for granted.
The 1999 National Day Golden Week marked the arrival of the era of mass tourism based on national consumption. It was an era where beautiful scenery surpassed food, and it was also a truly impoverished but genuinely happy era. As long as there is scenery to enjoy and historical sites to take photos of, no one will complain about group meals with eight dishes and one soup, nor will anyone care about simple meals with boiled water soaked noodles. In the past two decades, the proportion of catering in the total retail sales of consumer goods has been around 12%. Considering the sustained and rapid growth of the total social income and the relative stability of the consumer population, this data implies an increase in per capita consumption and an optimization of the consumption structure. 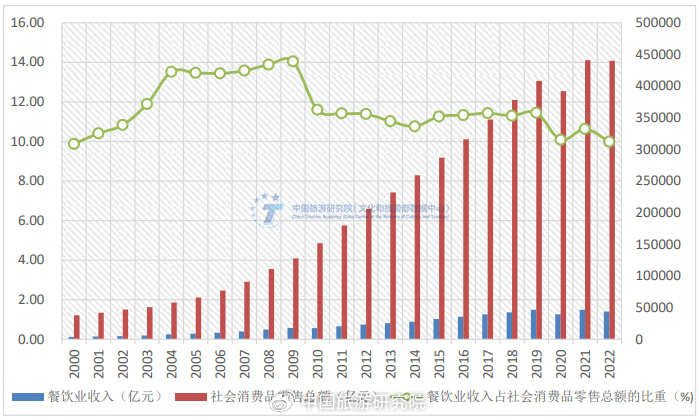
Figure 1 Changes in the proportion of catering industry revenue to the total retail sales of consumer goods in society
With more beautiful scenery and diverse scenes, the demand for delicious food begins to emerge. The reason why tourists complain about the "wall blocking the scenery" and "Xu Xiake is consumed by tickets when he can't walk a hundred miles away" in a fancy roast, and also complain about the "sky high shrimp" and "sky high yellow fish" angrily, is because of the awakening of the right consciousness, the rising proportion of catering and tourism in the overall consumption, or that tourists become more sensitive to the price, and the right consciousness begins to increase. With the arrival of a new stage of comprehensive development of mass tourism, more and more individual and self guided tourists are widely involved in the public leisure spaces of destination cities and rural areas, sharing local public services and commercial environments. The local breakfast, late night snacks, and various restaurants provide more choices for domestic tourists' stratified consumption, and vividly illustrate the warmest and most ordinary quality of life in the vast world, providing a stock optimization path for the high-quality development of the tourism industry. As tourism increasingly becomes a rigid demand in people's lives, quality and diversity will become new trends in tourism consumption, including catering, and provide new possibilities for business innovation and destination construction.
Column 1: Cognitive changes in food tourism
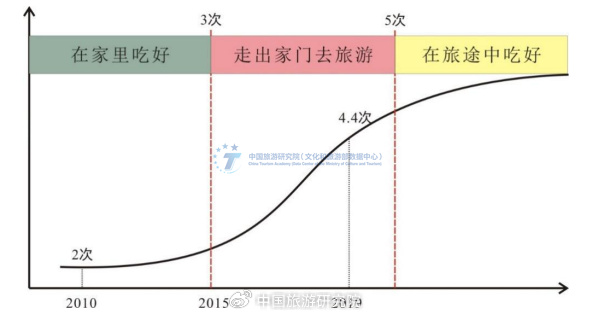
In the past twenty years, China's tourism industry has adapted to changes in tourism demand and presented stage characteristics. The boundaries of the tourism industry have become more open, from group sightseeing tours led by travel agencies to individual tourist markets supported by travel service providers and resource providers, and to the coexistence of personalized and diverse tourism demands. From the perspective of the development of international and domestic tourism, the resident travel rate shows an "S" - shaped curve. In the early stage of mass tourism, where the average annual travel per person is less than 3 times, the growth rate is slow, and sightseeing is the main focus. The need for food and beverage remains in the primary stage of being full, "eating well at home and playing well outside". In the comprehensive development stage of mass tourism, where the average annual travel per person is 3-5 times, the growth rate is fast and the demand is diverse. When traveling outside, not only do you need to eat well, but you also need to eat well. In the mature development stage of mass tourism where the average annual travel per person exceeds 5 times, the growth rate is slowing down, the demand is upgrading, and the demand for food in the itinerary is rapidly and widely increasing. Tourists should not only appreciate the beautiful scenery during their itinerary, but also experience the wonderful life of the tourist destination.
Figure 2: Food Demand and Evolution in Various Stages of Mass Tourism
Food is both a science and an art, often closely related to the development level of local economy, society, technology, and culture. The social status of chefs, bartenders, and banquet designers is also directly related to the consumption level of local residents and foreign tourists. Looking at the global tourism economy map, we can observe the differences in tourism cuisine among different countries and regions. Economically and socially developed countries and international metropolises are more willing to showcase contemporary living, including cuisine as a representative. Michelin restaurants and their managers often become the image representatives of the tourism industry, as well as an important driving force for industrial upgrading and brand cultivation. Underdeveloped countries and regions mainly promote natural scenery and cultural heritage, while catering tends to showcase traditional cuisine and local ingredients, with a relatively low level of industrialization. The cuisine of metropolises attracts tourists from all over the world due to their strong economic foundation and cultural confidence, while traditional tourist destinations rarely receive cultural premiums beyond procurement and processing costs. Today, the widespread flow of globalized capital, technology, culture, and tourists on a global scale is changing the old order of tourism and catering at an unprecedented speed and intensity, and reconstructing a new pattern of food tourism.
2、 Natural evolution of catering, innovative cuisine in the market, and government coordinated branding
Traditional food tourism is represented by the eight major cuisines and distinctive cuisine, emphasizing local characteristics and cultural heritage. People often say that watching the scenery is better than listening to it. Listening comes before watching, and the same goes for dining. Many familiar ingredients, cooking techniques, and dishes have spread to foreign lands through poetry, songs, movies, and modern media. Fresh seafood from Guangdong, hotpot from Chengdu and Chongqing, beef noodles from Lanzhou, the Eight Treasures of Water in Jiangnan during spring and summer, Shanxi's noodles that are not repeated 365 days a year, Nanjing's duck swimming across the Yangtze River, no chicken flying out of Zaozhuang alive, and so on, are not only folk jokes, but also a real food map in the eyes of the people. Just like some people travel with mountains and rivers, some travel with cultural heritage, and naturally some travel with food. Due to the influence of multiple factors such as region, soil, and seasonality, it is difficult for food to be delivered to the dining table through industrial production and modern logistics. As a result, distant cuisine has become more important for tourists' destination choices, and tasting seasonal ingredients at the destination has become a practical choice for more and more people. For example, seafood, we have heard from leaders in many places that they are the only seafood. If you travel one or two hundred miles inland, you will be considered seafood. As for what is bought from the market in major cities in mainland China, it can only be called seafood. It is precisely because of regional and seasonal characteristics that tourists who pursue timely ingredients travel around the world like migratory birds. If we string together the footprints of these 'food wanderers', it will be the real food route. In fact, market-oriented and productized food routes have always been created through eating and walking, rather than drawing them on a map while sitting in a study. Now it seems that the development model of food tourism driven by traditional cuisine and specialty foods is also in the stage of spontaneous growth. Food culture has not truly become the basic color of destination image construction, and food resources have not received the due evaluation and systematic development, especially the industry chain and ecosystem of food tourism have not been effectively constructed.
Column 2: Changes in Food Tourism Routes
A survey conducted by the Food Tourism Research Group of the China Tourism Research Institute found that 92.3% of respondents would make food guides before/during their travels; 93.1% of respondents consider experiencing local cuisine as one of the main factors for traveling to other places; Among the respondents who travel for business, 76.8% will squeeze in time to explore local cuisine outside of completing business. Food tourism is closely related to the flow of tourists, and it is also the market foundation for the layout of food tourism nodes and the development of routes.
Adjacent provinces present each other as both source and destination. In the domestic tourist flow, the proportion of high-speed rail, civil aviation, and self driving travel continues to increase, while the proportion of road passenger transportation continues to decline. In 2019, out of the top 100 inter provincial tourist flows, 64 were between adjacent provinces, while only 36 were between non adjacent provinces. The exchange of tourists between urban agglomerations constitutes the "main line" and "branch line" network of domestic tourism flow. The top 10 inter provincial tourism flows in the country account for 16.5% of all 930 inter provincial tourism flows, forming the "mainline" of inter provincial tourism flows in the country. The inter provincial tourism flows ranked in the top 11-100 nationwide account for 38.6% of all 930 inter provincial tourism flows, forming the "branch line" of the national inter provincial tourism flows. It constitutes the core support of the national inter provincial tourism flow network.
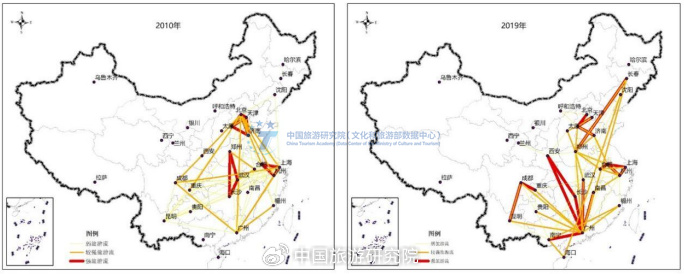
The tourism flow network has transformed from a "central agglomeration" of large areas to a "peripheral divergence" with core cities as nodes. In 2010, the TOP100 inter provincial tourism flows presented a "diamond shaped" network spatial pattern with the Bohai Rim, Yangtze River Delta, Pearl River Delta, and Chengdu Chongqing regions as the vertices, the central region as the core, and inter regional tourism connections as the skeleton (Figure 3). In the past decade, the peak flow of inter provincial tourism has begun to extend westward and northward, forming a divergent spatial pattern with cities as the vertices, fully radiating to the northeast and central western regions. Cities are not only the most important source market, but also the most important tourist destinations. Relying on cities and driving supply side reforms through demand side management is an important path to comprehensively promote high-quality development of the tourism industry in the new era, and it is also a strategic support point for food tourism.
Diagram 3: Evolution of Spatial Pattern of TOP100 Inter provincial Tourism Flows in the Past 10 Years
In the past 20 years of mass tourism, the flow of food tourists between urban and rural areas has been very uneven. From 2000 to 2010, the flow of food tourism mainly shifted from rural areas to cities. From 2010 to 2020, the two-way flow of food tourism between urban and rural areas began to increase, and overall it was still dominated by the flow from rural areas to cities. After 2020, due to the impact of the epidemic, long-distance tourism was hindered, and close range tourism and close to home leisure became mainstream for a certain period of time, further enhancing the flow of food tourism between urban and rural areas. With the comprehensive recovery of tourism activities, seeking differentiated food experiences between urban and rural areas will become a trend, and the intensity and frequency of mobility will increase.
....
Contemporary food tourism is more of a result of commercial innovation such as capital, technology, and creative promotion. With the progress of the times and the pursuit of science, health, and modern lifestyle by the people, cuisine derived from traditional agricultural civilization can no longer meet the needs of contemporary tourism experience. Tourists should not only have delicious food at their destination, but also eat healthier, more eco-friendly, and more balanced food. Demand is business opportunity. Driven by capital, technology, and cultural creativity, Changsha Wenheyou, which focuses on nostalgia, Haidilao, which offers ultimate service, Beijing Banquet, which combines business etiquette and cultural heritage, as well as the popular young people's favorite Cha Yan Yue Se, Xi Cha, Mi Xue Bing Cheng, Maotai, and Luckin Coffee's sauce flavored latte, will all become tourist destination food check-in points. It is worth noting that in international metropolises such as Shanghai, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, and Beijing, international catering brands have widely entered the local food map, becoming a new highlight of food tourism. Whether it is McDonald's and KFC, which are aimed at the public, or Beijing Jingzhaoyin, which is on the Michelin list, Shanghai UV UV, and Stiller from Guangzhou Garden Hotel, they have all become contemporary food new spaces that are close to home and shared by guests with international standards and fashionable atmosphere. Compared with traditional cuisine and specialty dining, contemporary cuisine is often a product of the collusion between demand and supply. Although every Michelin ranking release will trigger different voices, the era of "I make my own decisions on my itinerary, and I make my own decisions on my cuisine" has irreversibly arrived. Many times, tourists eat delicious food, experience fashion and individuality, and pursue a personalized lifestyle. Once the era of deep integration between food and tourism begins, whether we are willing or unwilling, the business restaurants in high star hotels, social restaurants in commercial districts, and breakfast snacks scattered throughout the community will inevitably be impacted and transformed by the demand of foreign tourists. The "non authentic" in the eyes of the older generation will be a market reality that the catering industry has to accept.
Column 3: A New Food Space Shared by Guests and Guests
The spatial layout of catering facilities has a high spatial correlation with the spatial layout of cultural, commercial, and leisure facilities. The spatial correlation between Macau's catering layout and leisure facilities is over 90%, while the spatial correlation between Beijing's catering layout and cultural and commercial facilities is 73%. Those internet famous dining check-in points that have been selected for Michelin, Black Pearl, and Gourmet Forest rankings and have strong market appeal not only do not have exclusive spatial distribution, but are highly related to cultural, commercial, and leisure atmosphere. They cluster together in layout and gather in space, ultimately presenting themselves as food and beverage blocks or complexes.
The spatial correlation between dining and leisure facilities on the Macau Peninsula, as shown in Figure 4
The spatial correlation between catering facilities and cultural and commercial facilities in Beijing, as shown in Figure 5
Food tourism also shows certain spatial patterns at the regional scale. Regions with strong food culture origins, complete commercial supporting facilities, and strong potential for residents to travel are also relatively concentrated in food tourism. The country has presented four major food tourism clusters: the Bohai Rim, Yangtze River Delta, Pearl River Delta, and Chengdu Chongqing. By comparing the catering revenue and customer source output of each province through spatial fitting, the spatial fitting degree is about 70%, and the short - to medium-term customer sources support the development of food tourism in the destination.
.....
With the joint efforts of cultural, tourism, business, broadcasting and other departments, the development of regional food tourism brands has entered a new stage led by the government. Food, accommodation, transportation, tourism, shopping, and entertainment are the priority elements of tourism development. With the transformation of tourism space from scenery to scenery, the position of catering and cuisine in the construction and development system of tourist destinations has become increasingly prominent. The "Hundred Counties and Thousand Bowls" in Zhejiang, the "Taste of Hunan: A Taste of Hunan" in Hunan, the "Beautiful Taste of Anhui, Famous Snacks of Hundred Counties" in Anhui, the Guangzhou Asian Food Festival, Qingdao Beer Festival, Jinan Shandong Cuisine Food Festival, as well as the food promotion cases of major star rated hotels, have shown that food has been incorporated into the strategic vision of local tourism development, becoming a new driving force to promote tourism consumption and high-quality development of the tourism industry. In addition to food variety shows such as "Chinese Restaurant", "Heard it was delicious", "strip the skewers Bar", and the blessing and promotion of food broadcasters such as Tiktok, Xiaohongshu, and Station B, an era of food tourism competition has begun. In terms of effectiveness, food tourism has basically completed the concept introduction, but the business model of food tourism still needs to be explored, and market practice still needs innovation. Food festivals and tourism promotion in various regions still rely on local characteristics and traditional cuisine, innovative cuisine that adapts to the fashion experience of contemporary tourists, especially the attention of restaurants and food hosts, is not enough. Compared with countries such as Singapore, Japan, Spain, France, Italy, which elevate food to the destination image support, and emphasize the promotion of scenic spots, resorts, and leisure blocks, most places' food tourism is still in the primary stage of auxiliary and supplementary, let alone top-level design for the cultivation, construction, and promotion of food tourism at the national level. There is no innovative synergy for the tourism market between the cultural and tourism and business departments, government departments and market entities, and catering enterprises and travel merchants. In fact, we still have a long way to go from experiencing food in a city to visiting a city for the sake of food experience.
3、 Respect the market, take the initiative, and create a new pattern of Chinese style food tourism
One is to cultivate urban and rural nodes for food tourism, relying on cities, especially modern comprehensive cities dominated by economic population and supplemented by non economic population, to cultivate a number of food tourism cities and blocks, supplemented by key tourist villages and towns, and thus form spatial support for food tourism. Traditional cities prioritize growth as political and cultural centers, while modern cities prioritize growth as industrial and commercial trade centers. The activities of industry, commerce, economy, trade, and science and education have brought a large number of mobile populations from home and abroad, forming the necessary endogenous consumption foundation for the development of food tourism. They have also provided innovative momentum for the promotion of regional food tourism, such as Michelin restaurants in Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangzhou, as well as food districts in cities such as Changsha, Hangzhou, and Nanjing. If there is no local consumption base and upgrading of the consumption of the business class, relying solely on the basic catering needs of sightseeing and leisure tourists, it is difficult to become a spatial node for food tourism.
The second is to rely on high star hotels and socially influential social catering to cultivate market entities and product brands for food tourism through classification. Influenced by the traditional tourism model of "sightseeing teams", some places are accustomed to using designated restaurants as the driving force for food tourism, and drawing on the standardized model of star rated hotels and A-level scenic spots to classify tourism catering. However, it has been proven that this path is not feasible. A feasible approach is to leverage the power of mass media and corporate marketing, take the path of market-oriented development, guide high star hotels and government reception hotels to cultivate high-end banquet and specialty catering brands and open them to society, such as Shangri La's Hutong, Garden Hotel's Taoyuan Branch, or introduce brands such as Junting, Xingmu, and Lantian Earl to form a high-end catering center. A more feasible approach is to leverage the role of urban lifestyle integrated media and variety shows, promote local specialty restaurants to the tourism market, and transform local cuisine into tourism cuisine through word-of-mouth communication.
Thirdly, we should focus on leveraging the role of travel agencies, online travel platforms, and new media platforms to encourage more tourists to include food in their urban and rural tourism destination guides. Some provincial and municipal tourism departments have launched "must eat lists", which are beneficial attempts to promote the tourism market and build destinations. It seems that it is not enough now. In order to attract more tourists to visit a city for their favorite food and dining, it is even more important to use modern tourism development concepts to make food a concrete support for urban tourism. Above the landscape lies life, and the tourist destination is the sum of the living environment. This is a new concept in the development of modern tourism. We go to see the cities in the eyes of tourists, such as Guangzhou. The top five keywords are the Pearl River, Chimelong, Xiaomanyao, morning tea and sugared water, as well as the hotpot in Chengdu and Chongqing, and the night market in Changsha. What can leave a lasting memory and be willing to revisit are these warm fireworks in the world. The food journey is first and foremost a leisure trip within the city. In the Netherlands, there is a food culture street where each restaurant tastes a dish. In Beijing, there are also travel merchants designing such products, but overall it is still in the spontaneous stage. We can strengthen cooperation with institutions such as Ctrip, Meituan, Mafengwo, Xiaohongshu, and "Chinese Restaurant" to productize and route food tourism, allowing tourists to experience culture through tasting food from near to far, from niche to popular, and forming a group of market driven and tourist recognized food tourism routes.
The fourth is to strengthen cooperation between the cultural and tourism systems and departments, and to study and release guidance on accelerating the development of food tourism. With the improvement of people's living standards and the enrichment of tourism experience, tourists not only need to have delicious food at their destination, but also fresh, ecological, healthy, and culturally rich food. To achieve this goal, we cannot do without the support of agriculture, industry, and commerce departments, as well as the basic support of thousands of enterprises in the catering industry chain from production, logistics, processing, service, and sales. We also cannot do without the guidance of culture, art, and fashion. Whether it's the idea of pure bass or the combination of body and soil, what we eat is not just the ingredients themselves, but also the quality of life and cultural tone. On this basis, we will guide local governments and enterprises to strengthen international cooperation with Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan, and use multilateral mechanisms and social forces to launch brands such as "East Asia Food Tourism City", "the Belt and Road Food Tourism Tour", "Welcome China - Food Restaurant", "Hello, China - Food Tour", to help promote international promotion and quality improvement of food tourism.
Author | Dai Bin
Manuscript Review | Yang Liqiong
Source | China Tourism Research Institute (Data Center of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism)
Please indicate the author and source when reprinting