Jiaxing has dense ancient towns, high market awareness, mature development, and rich experience in innovation, which have significant advantages in the development of ancient town tourism nationwide. After years of development, the Jiaxing Municipal Party Committee and Government are determined to establish the brand image of "China Ancient Town Looking at Jiaxing". As a government think tank and industry think tank, China Tourism Research Institute has accumulated rich experience in cultivating new tourism formats and shaping tourism brands in recent years, and has the advantage of utilizing professional capabilities for specialized research. Based on this background, the Jiaxing Municipal Bureau of Culture, Radio, Television and Tourism commissioned the China Tourism Research Institute to conduct research on ancient town tourism, hoping to grasp the quantity, spatial distribution pattern and market characteristics of ancient town scenic spots in China from a macro level, and analyze the development level of ancient town tourism in China from the perspective of tourists. The report shows that both the quantity and quality of ancient town scenic spots, as well as the level of development of ancient town tourism, indicate that Jiaxing City has the foundation and conditions to lead the development of ancient town tourism. The core points of the report are as follows:
1、 The spatial distribution pattern and characteristics of ancient town tourism
(1) Spatial distribution pattern of ancient town scenic spots
The number of ancient town scenic spots gradually decreases from southeast to northwest in China, and the "Hu Huanyong Line" has become the geographical boundary for the distribution of ancient towns. According to the statistics of the research group on the sample ancient towns, 95.7% of the ancient town scenic spots in China are distributed in the areas east and south of the "Hu Huanyong Line".
There are dense ancient town scenic spots in provinces such as Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, Jiangxi, and Sichuan Yunnan. From the number of sample ancient towns in each province, the national ancient town scenic spots are mainly concentrated in provinces such as Sichuan, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Anhui, Yunnan, and Jiangxi. The number of ancient town scenic spots in the six provinces is 36, 27, 21, 21, 19, and 17, respectively. Overall, with 14.5% of the country's land area, more than half of the country's ancient town scenic spots are gathered; The number of ancient town scenic spots in Gansu Province, Hubei Province, Jilin Province, Liaoning Province, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Beijing, Hainan Province, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Qinghai Province, Tianjin, Xizang Autonomous Region, Heilongjiang Province and other provinces accounted for less than 2%.
The clustering characteristics along the Yangtze River are significant, and ancient towns are densely distributed along the Beijing Hangzhou Grand Canal. The local concentration characteristics of ancient town scenic spots in the country are significant, forming highly concentrated areas of ancient town scenic spots in southern Jiangsu, northern Zhejiang, southern Anhui, western Zhejiang, southeastern Sichuan, and northwestern Yunnan, showing a regular pattern of decreasing ancient town density from this region to surrounding areas. Especially in southern Jiangsu and northern Zhejiang, the density of ancient town scenic spots is the highest, and it gradually decreases towards southern Anhui, western Zhejiang, and surrounding areas. Looking at these highly concentrated ancient town scenic areas, they are mostly distributed in areas with high population density and rich river networks. The characteristics of ancient towns distributed along the river are significant. According to statistics, there are more than 80 representative ancient towns distributed along the Beijing Hangzhou Grand Canal. Among them, the ancient towns are relatively evenly distributed along the Tonghui River, North Canal, South Canal, Lu Canal, Central Canal, Li Canal and other river sections, while the ancient towns along the Jiangnan Canal are dense. Overall, as a dual overlapping area of the Yangtze River Basin and the Jiangnan Canal, the Jiangnan region has become the main area for the distribution of high-quality ancient town scenic spots, especially in China.
5A level ancient town scenic spots are highly concentrated in the Jiangsu Zhejiang Anhui region. According to statistics, there are currently 33 5A level ancient town scenic spots in China. In terms of spatial distribution, Zhejiang Province ranks first among all provinces with five ancient town scenic spots: Xitang Ancient Town, Wuzhen Scenic Area, Nanxun Ancient Town, Erbadu Ancient Town, and Taizhou Fucheng, followed by Anhui Province and Jiangsu Province, all of which have four 5A level ancient town scenic spots. The number of 5A level ancient town scenic spots in Zhejiang Province, Anhui Province, and Jiangsu Province accounts for 39.4% of the national total. 5A level ancient town scenic spots are highly concentrated in the Jiangsu Zhejiang Anhui region.
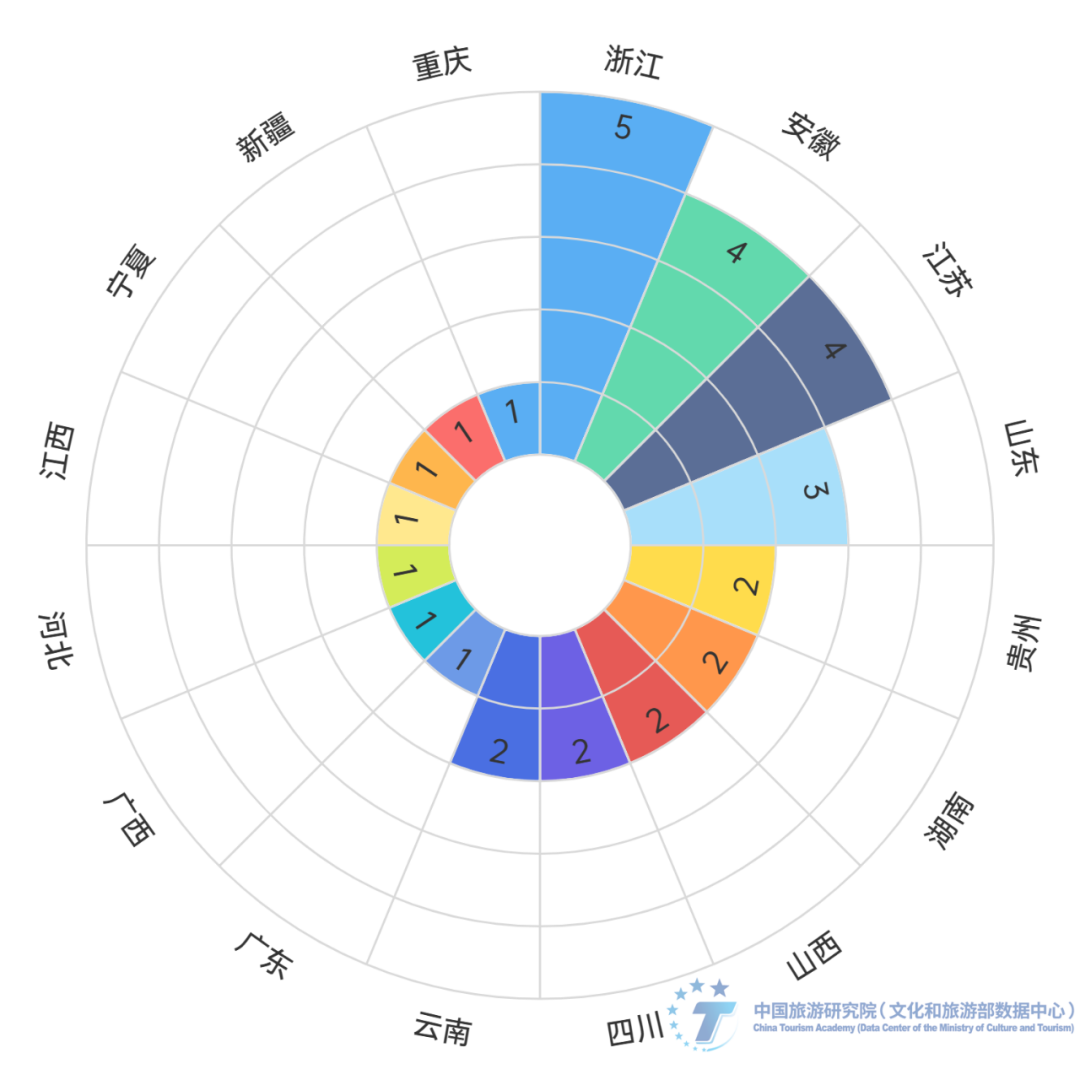
Figure 1: Number of 5A level Ancient Town Scenic Spots in Each Province Source: Collected and Organized by the Research Group (II) Characteristics of Tourist Source Distribution in the Ancient Town Tourism Market
Provinces with strong economic strength and large population base have a wider coverage of residents traveling to ancient towns. According to the customer source data of various sample ancient town scenic spots, residents from 12 provinces (cities) including Guangdong Province, Shanghai, Zhejiang Province, Beijing, Jiangsu Province, Henan Province, Sichuan Province, Hubei Province, Shandong Province, Fujian Province, Hunan Province, and Anhui Province visited more than 200 sample ancient town scenic spots between October 2023 and March 2024. The tourism footprint of residents in Guangdong Province covers 88.9% of the ancient town scenic spots in China, while residents from Shanghai, Zhejiang Province, Beijing, Jiangsu Province, and Henan Province have visited more than 80% of the ancient town scenic spots. In contrast, the coverage and activity of residents visiting ancient towns in the Xizang Autonomous Region, which is located in the southwest, and provinces in northeast and northwest China are low.
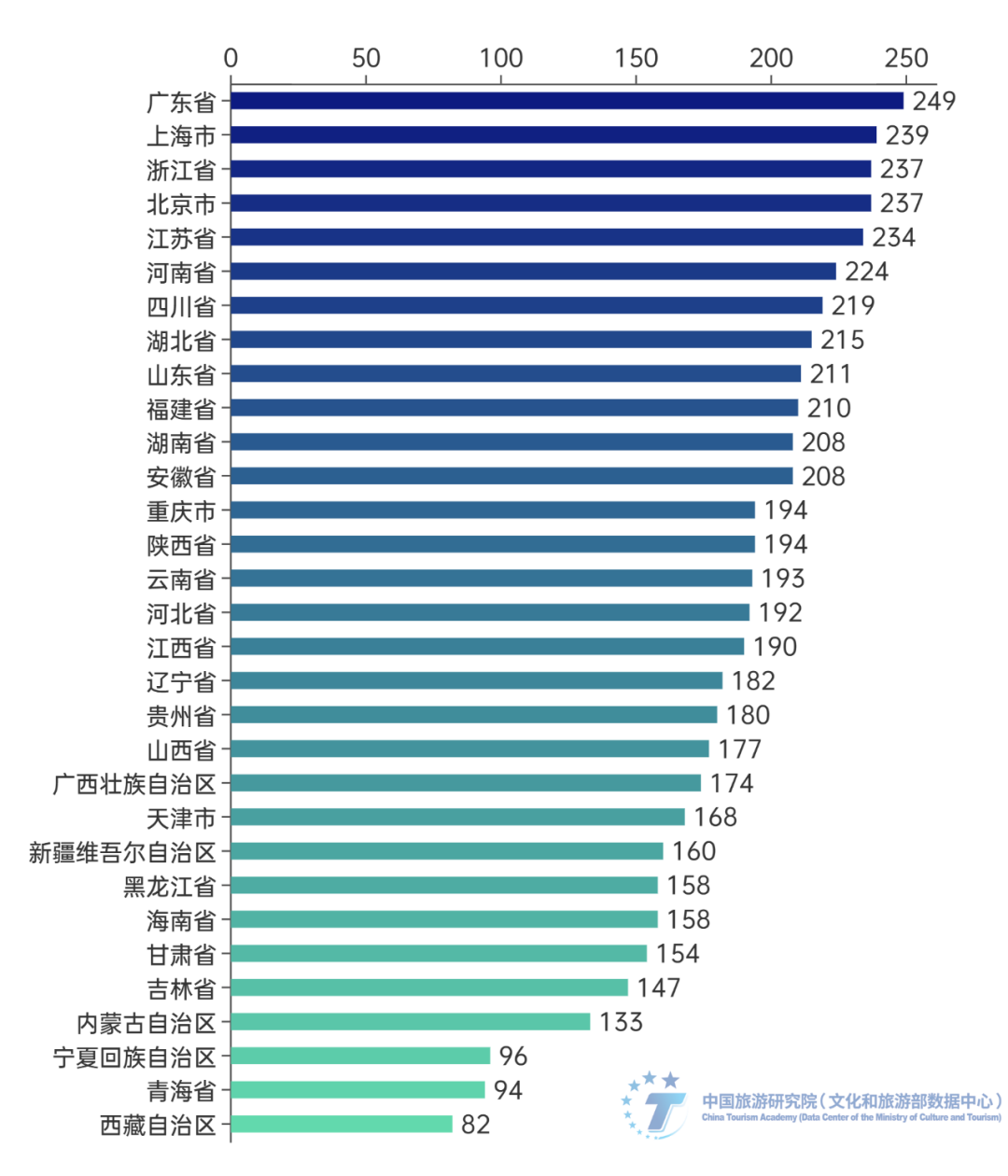
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of the number of ancient towns sampled for residents' travel in each province
Data source: The research team collected and organized data
The ancient towns in East China have stronger popularity and appeal to the external customer market. From the perspective of reception, this study compared and analyzed the customer sources of provinces with six or more ancient town scenic spots. It was found that provinces such as Sichuan, Yunnan, Chongqing, and Guizhou, located in the southwest region, had a relatively high proportion of customer sources within the province. However, the proportion of customer sources within Zhejiang, Jiangsu, and Jiangxi provinces in East China was significantly lower, indicating that ancient town scenic spots in East China have a stronger attraction to tourists from other provinces and a broader market for customer sources outside the province. In addition, economically developed and densely populated provinces (cities) such as Guangdong Province and Shanghai have an absolute dominant position in the out of province tourist market for their ancient town scenic spots (Figure 3). From the perspective of travel, Guangdong Province, Jiangsu Province, Zhejiang Province, Shanghai City, and Sichuan Province have an absolute advantage in leading cross provincial ancient town tourism, forming the main source market for cross provincial ancient town scenic spots (Figure 4). 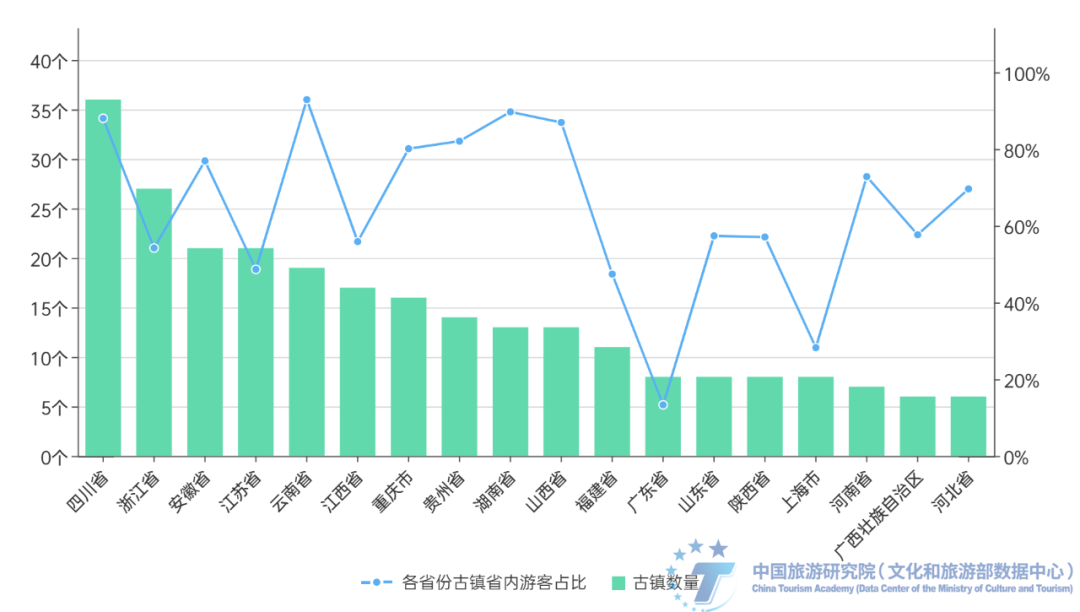
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of the proportion of total customer sources in the sample ancient towns of each province. Data source: The research team collected data and organized it
Figure 4: The proportion of people traveling to ancient towns outside of each province to the total number of cross provincial ancient town tourists in China. Data source: The research team collected and organized data. 2. Ancient Town Tourism Development Index Tourism, based on the premise of tourist visits. In the context of "tourists defining the tourism industry", the development index from the perspective of tourists has more practical significance. Based on this, this study constructs an index system from three levels: pre visit search popularity, in visit popularity, and post visit satisfaction, from the perspective of tourists, to study the ancient town scenic area. (1) The spatial distribution of the ancient town tourism search heat index in China shows a clear "core edge" structure: the Jiangnan region is a first level core hotspot area, the border between Shanxi, Hunan, Guizhou, and Chongqing constitutes a second level core hotspot area, and the northwest of Yunnan is a third level core hotspot area. The heat index gradually decreases towards the surrounding areas in the order of first, second, and third level core hotspots. From the top 10 ancient towns in terms of search popularity index, the Jiangnan region holds 4 seats, namely Zhouzhuang, Wuzhen, Nanxun, and Xitang located in southern Jiangsu and northern Zhejiang. It can be seen that the ancient water towns in Jiangnan have won the favor of a large number of tourists with their leisurely living atmosphere and comfortable climate environment, and are a type of ancient town that potential tourists are paying close attention to. In addition to Zhouzhuang, Wuzhen, Nanxun and Xitang, there are also Phoenix Ancient City, Pingyao Ancient City, the Old Town of Lijiang, Gubeishui Town, Taierzhuang Ancient City and Langzhong Ancient City, which are distributed in Hunan, Shanxi, Yunnan, Beijing, Shandong, Sichuan and other provinces, covering different types of ancient town scenic spots such as ancient villages in the southwest, courtyards in the north, and ancient villages in Nanzhao, fully reflecting the diversified needs of potential tourists. (2) There is a slight difference between the tourist attention index and the search popularity index of ancient town scenic spots. The OTA platform tourist attention index forms a relatively dispersed "multipolar" spatial distribution pattern in the Jiangnan region, southeastern Sichuan, northwestern Yunnan, the border between Hunan and Guizhou, and Shanxi. From the distribution of tourist attention index TOP10 ancient towns, the Old Town of Lijiang, Dali Old City, Ciqikou ancient town and Qingyan ancient town in southwest China occupy 4 seats; Zhenbeibao Ancient City is among them, which is closely related to the extensive practice of the "film and television+cultural tourism" model in recent years, demonstrating the powerful momentum released by the integration of culture and tourism. (3) The popularity index of ancient town tourism is derived from the core density distribution of the popularity index of ancient town scenic spots. Ancient town tourism has initially formed a high-density "C" - shaped popular gathering area with Jiangnan water towns as the polar core, composed of the border areas of Yunnan, Sichuan, Chongqing, and Hunan Guizhou, etc. The top 10 popularity index of ancient town scenic spots shows that Xitang, Nanxun and Wuzhen, the ancient towns in the south of the Yangtze River, are among them, and the ancient towns in the southwest area occupy five seats, namely, the Old Town of Lijiang, Ciqikou Ancient Town, Furong Town Scenic Spot, Anren Ancient Town and Jianshui Ancient City. (4) The satisfaction index of ancient town tourism is based on the density distribution of tourist satisfaction index in ancient town scenic areas. High satisfaction ancient towns are mainly concentrated in the border areas of Jiangnan water towns and Sichuan Chongqing Hunan Guizhou. Specifically, in terms of tourist satisfaction TOP10, Jiangnan Water Town Ancient Town occupies 5 seats, namely Wuzhen Scenic Area, Nanxun Ancient Town, Tongli Ancient Town, Xitang Ancient Town, and Zhouzhuang Ancient Town. Anren Ancient Town, Furong Town Scenic Area, and Langzhong Ancient Town in the southwest region are among them. (5) Summary of Ancient Town Tourism Development Index: The search popularity index, tourist attention index, popularity index, and satisfaction index mentioned above all indicate that ancient town tourism has formed a spatial development pattern of "multi-core agglomeration". The development level of different index "extreme cores" further characterizes that the ancient town scenic spots in Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Shanghai, Anhui, and Jiangxi regions exhibit spatial agglomeration characteristics of high development levels in terms of search popularity, tourist popularity, and tourist satisfaction, belonging to the first group and hotspot areas of ancient town tourism development in China. 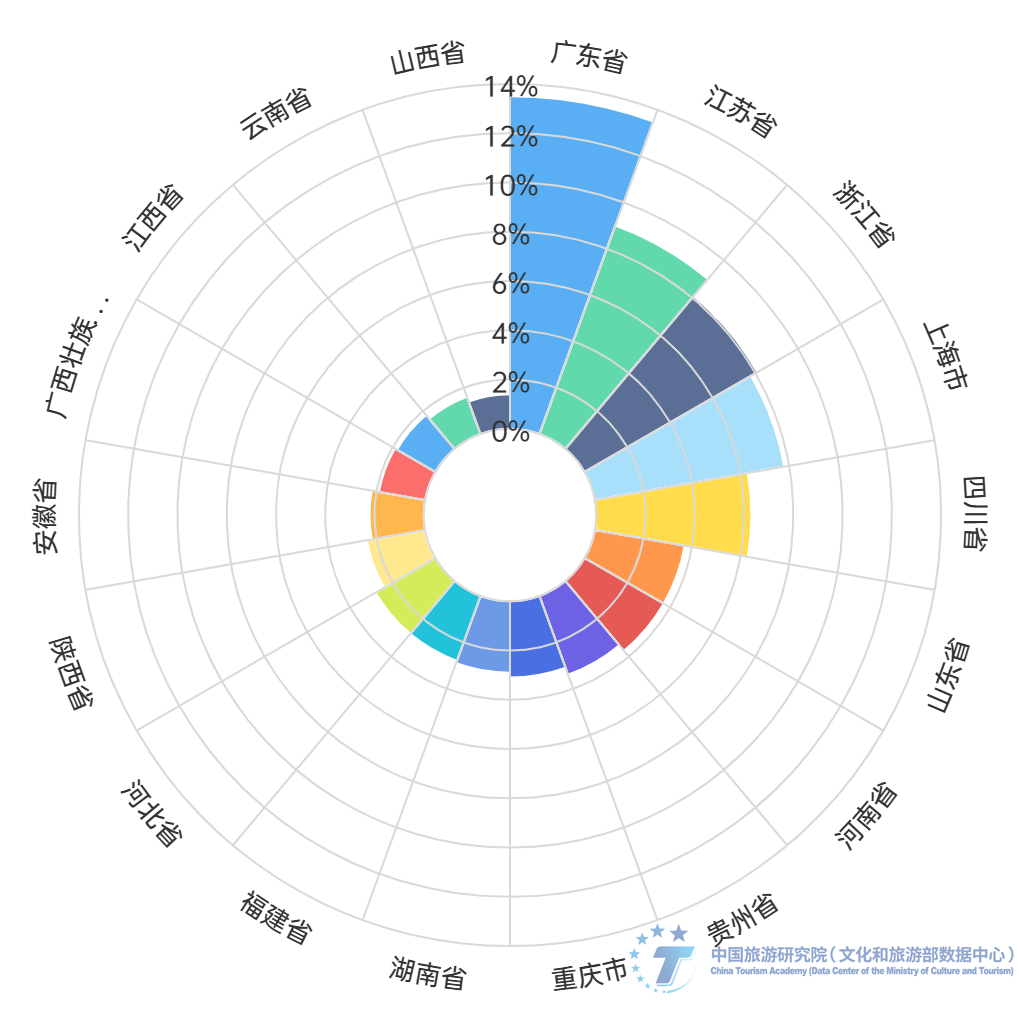
Figure 5 Top 10 Ancient Town Tourism Development Index
Data source: Data collected by the research group; Questionnaire survey data; Baidu and OTA platform data
Further focus on Jiaxing City, Zhejiang Province, which is located in the first tier. The city has a large number of ancient towns and rich types, including relatively mature Wuzhen and Xitang, as well as growing Puyuan and Yanguan, and a number of ancient town tourism resources with development potential such as Wangjiangjing, Xincheng, and Shendang. Whether viewed from a national perspective or the Yangtze River Delta region, Jiaxing has the foundation and conditions to lead the development of ancient town tourism in terms of the quantity, quality, and innovation of ancient town scenic spots. According to the research team's statistics, there are 33 5A level ancient town scenic spots in China, distributed in 29 prefecture level cities, with Jiaxing City occupying two seats, Wuzhen and Xitang. In recent years, Wuzhen has promoted Jiaxing Ancient Town to form a distinctive cultural brand with the drama festival, the World Internet Conference and various cultural activities as the carrier, Xitang has relied on activities such as the Hanfu Culture Week and the "Twelve Flower Gods", Puyuan has taken the development path of "ancient town+fashion+cultural tourism", and the development direction of salt officials with the theme of tide watching and music. The research results show that the search popularity, satisfaction, and OTA platform tourist attention index of Wuzhen Scenic Area are all in a leading position among the sample ancient towns, while Xitang is also ranked in the top 10 of multiple indices. Jiaxing Ancient Town leads the high-quality development of ancient town tourism with continuous innovation, meeting the diverse market's yearning for a better life. The basic pattern of "Chinese ancient towns looking at Jiaxing" has taken shape. 3、 Characteristics of Ancient Town Tourism Market Based on Sampling Survey (1) Strong Demand in Ancient Town Tourism Market Ancient town tourism is an important travel choice for tourists in the stage of mass tourism development. According to a special survey conducted by the research group, 93.4% of the respondents have participated in ancient town tourism, while only 6.6% have not been, indicating that ancient town tourism occupies an important position in the domestic market in China. A large number of tangible cultural heritage sites such as ancient villages, towns, and cities across the country are important travel spaces for domestic tourists and important targets for supply side protection and development. Among the respondents who have participated in ancient town tourism, 41.05% have participated in ancient town tourism once in the past two years, 40.35% have visited twice, and 9.66% have visited three times. It can be seen that over 80% of tourists have visited the ancient town once or twice in the past two years. It can be seen that in the long-term and short-term tourism with an average of 4.3 trips per person per year (2019 data), ancient town products are quite popular among tourists, and a large number of tourists will trigger ancient town tourism products during their 1-2 trips. 
Figure 6: The frequency and proportion of respondents who have visited ancient towns in the past two years (respondents who have participated in ancient town tourism). Data source: Sampling survey data from the research group. The leisurely living atmosphere and local cultural experience are the main tourism needs of tourists in ancient towns. Tourists are increasingly pursuing the emotional value and leisurely atmosphere in the ancient town space. Among the most attractive factors for respondents in ancient town tourism, a leisurely living atmosphere is the most popular, accounting for 27.1%; Next are architectural style and local specialty cuisine, accounting for 23.4% and 20.7% respectively; However, factors such as historical culture, folk activities, natural scenery, and environment gradually decrease the attractiveness to the respondents. At the same time, the survey shows that the main purposes of traveling to ancient towns are to relax, experience the slow life of the town (43.5%), appreciate the scenery, take photos for check-in or artistic creation (18.6%), and taste local specialty cuisine (30.7%). 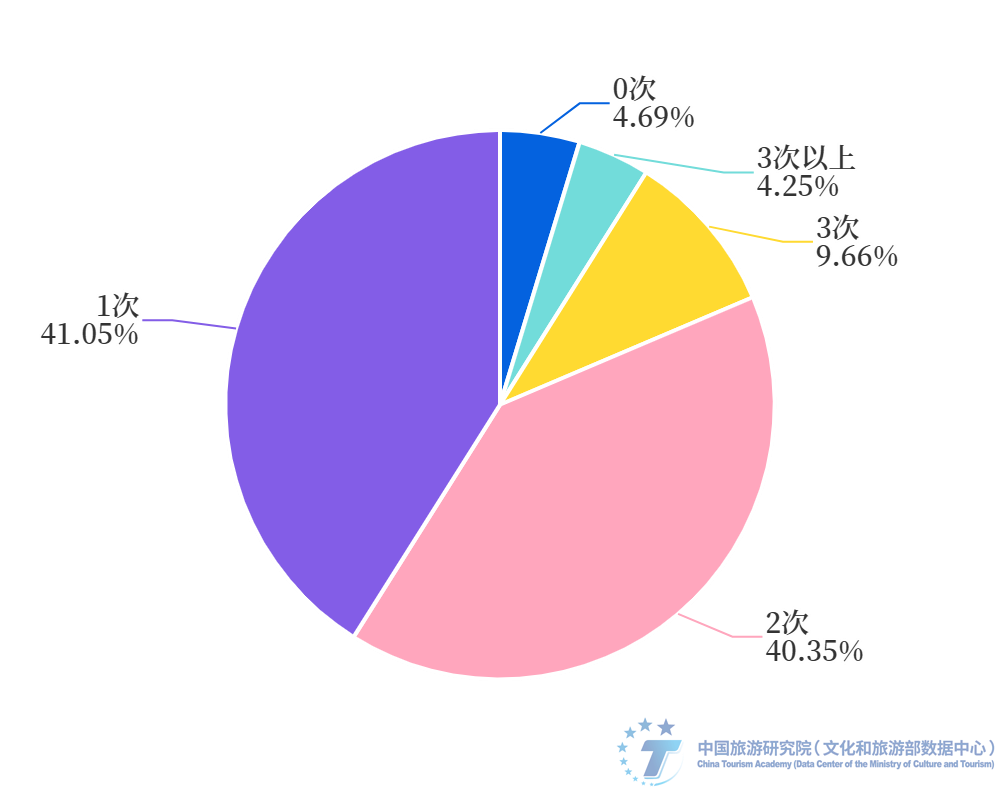
Figure 7: The most attractive factors for tourists in ancient town tourism
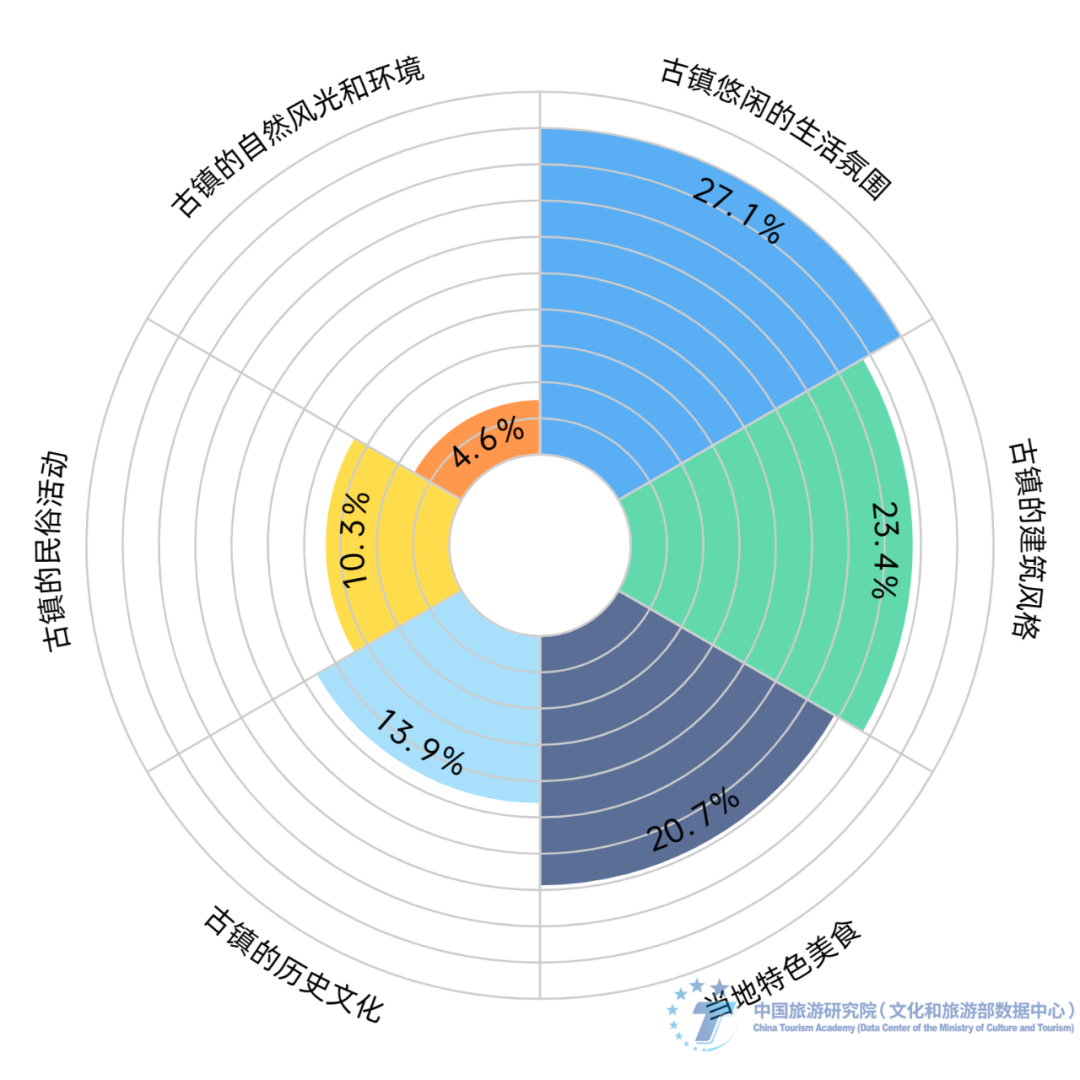
Figure 8: The main purpose of participating in ancient town tourism
Tourists have high demands and expectations for experiencing local culture. The services and experiences that respondents hope the public spaces in ancient towns can provide, in descending order, are traditional handicraft experiences (42.39%), local historical and cultural exhibitions (38.83%), and folk performances (31.15%). The proportion of choices for creative studios (16.6%), visual art bars (14.44%), digital leisure and entertainment (5.64%), and night tours of ancient towns (3.5%) is relatively low.
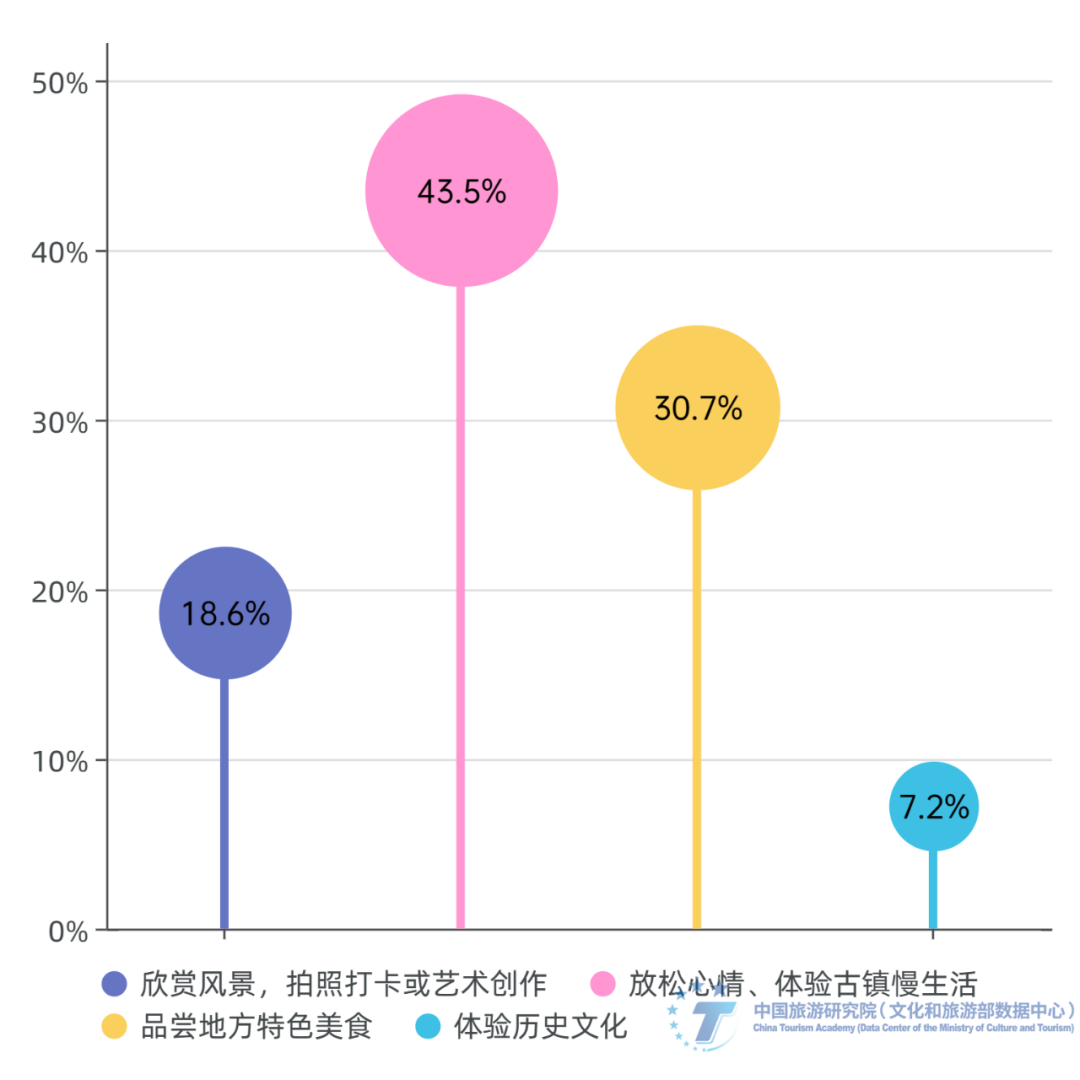
Figure 9: Service or experience options and proportion that respondents hope the public space in the ancient town can provide
(3) Traditional word-of-mouth communication and sharing are important channels for promoting ancient town tourism
Ancient town tourism relies more on pre visit "planting grass", and the reputation and satisfaction of scenic spots are the best "planting grass" channels. 51.58% of respondents will briefly understand basic information before traveling to ancient towns, and 35.39% of respondents will make detailed guides. The proportion of respondents who only focus on information such as transportation and accommodation is only 11.02%. This indicates that most tourists will learn relevant information before traveling to ensure a smooth and enjoyable trip. Therefore, for the operators of ancient town scenic spots and tourist destinations, the early stage of "planting grass" is more important. At the same time, the survey shows that tourists' access to tourism information in the ancient town mainly focuses on the recommendation of friends or family members, Ctrip, Mafengwo and other tourism websites or APP, as well as social media such as Station B, Tiktok, Little Red Book and Kwai. Among them, friends or family members recommended the highest proportion, up to 46.28%, followed by Ctrip, Mafengwo and other travel websites or apps, accounting for 31.44%, while the proportion of local official official account and cloud platform recommendations, travel agencies or travel guides was relatively low. It can be seen that the reputation of ancient towns is the best way to "plant grass". (4) Local cuisine in ancient towns is an important way for tourists to experience the atmosphere of different places. Local specialty cuisine is an important part of the experience in ancient towns, and its price and comfortable environment have a significant impact on tourists' experience. According to the survey, 66.02% of respondents like or really enjoy trying the local specialty cuisine of the ancient town, believing that it is an important component of experiencing the ancient town culture. When choosing a restaurant in an ancient town, the most important factor for respondents is whether the price is reasonable, accounting for 46.41%. Next is the comfort level and cultural atmosphere of the dining environment, accounting for 40.64%. The taste and characteristics of food are also important considerations, accounting for 32.4%. At the same time, ancient town style restaurants are the preferred type of dining for respondents, accounting for 49.97%, followed by specialty snack stalls, accounting for 27.12%. The proportion of choosing star rated hotels or high-end restaurants is relatively low, only 2.04%. 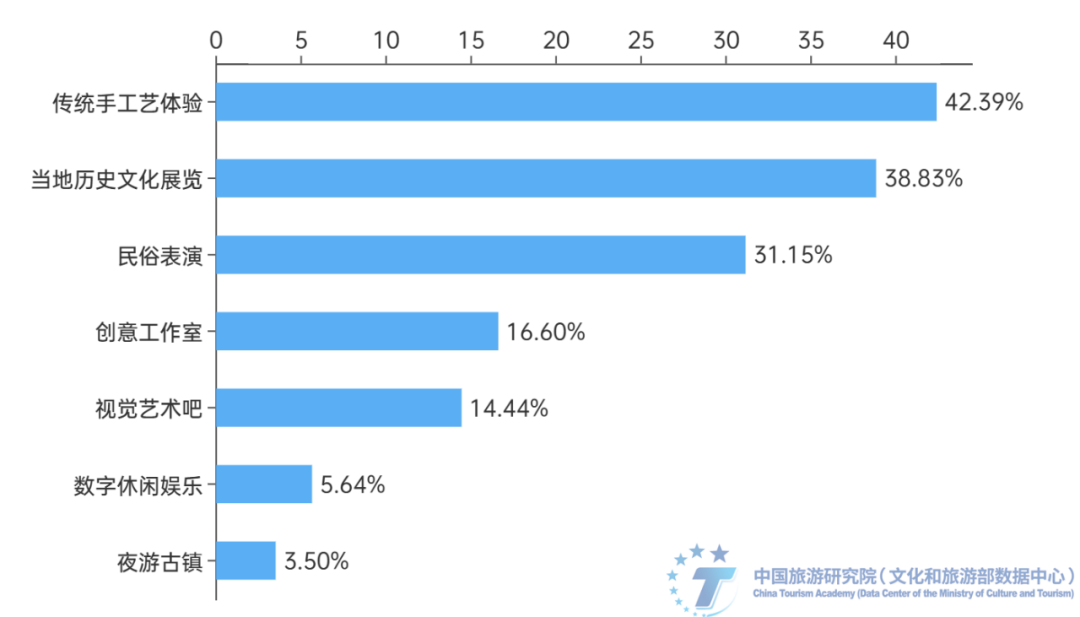
Figure 10: Proportion of respondents who enjoy trying local specialty foods or snacks in ancient towns
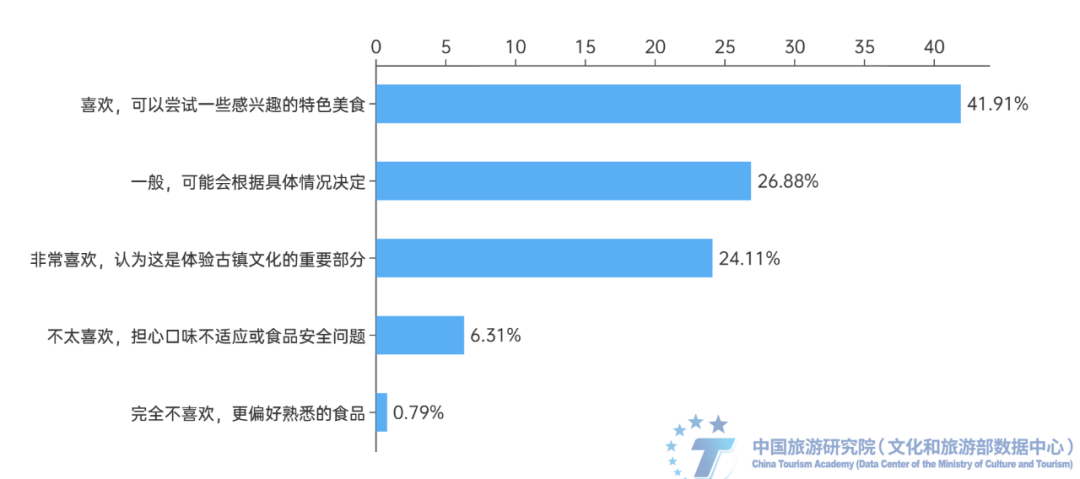
Figure 11: The factors and proportion that respondents value the most when choosing a restaurant in an ancient town
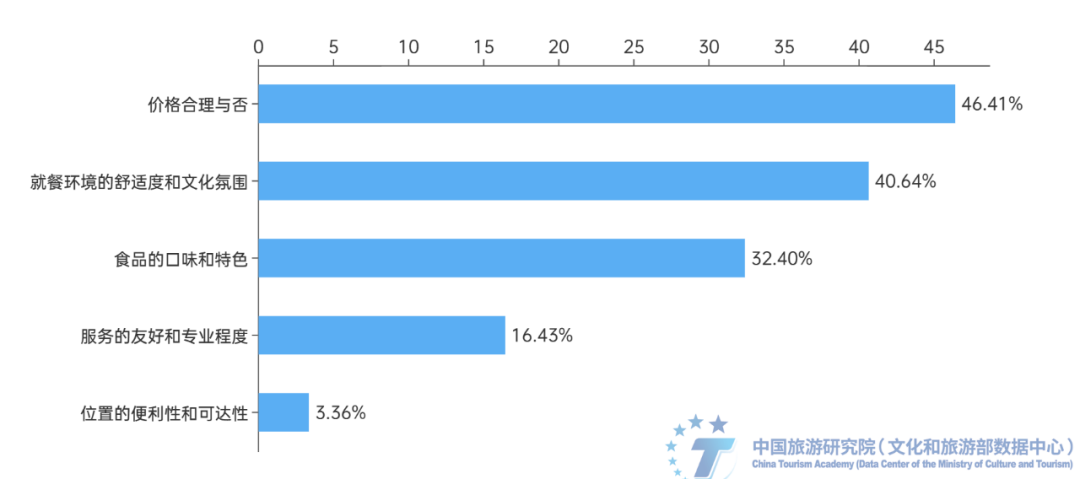
Figure 12: The proportion of respondents who choose different types of dining venues in ancient towns
(5) Most tourists prefer comfortable and distinctive accommodation experiences in ancient towns. The comfort and uniqueness of accommodation in ancient towns are important criteria for tourists to choose. Data shows that 81.76% of respondents would choose to live in an ancient town, while 18.24% of respondents would choose to live near or outside the town. The preference for accommodation types in ancient towns is mainly concentrated in star rated hotels or chain hotels (40.95%) and specialty themed hotels (35.17%), accounting for a large proportion of respondents respectively. The proportion of traditional guesthouses or homestays is 17.86%, slightly lower than the previous two. The selection ratio of youth hostels or backpacker hostels is only 6%. Overall, the choice of accommodation types in the ancient town tends to be more inclined towards star rated hotels or chain hotels that pursue comfort and convenience, as well as themed hotels with distinctive features. Among the reasons for choosing not to stay in the ancient town, 48.55% prefer to live slightly away from the scenic spots and enjoy a peaceful environment; 34.15% of accommodation facilities are more convenient and complete; The price factor accounts for 29.35%. Meanwhile, 71.26% of the respondents chose accommodation prices ranging from 200 to 600 per night.
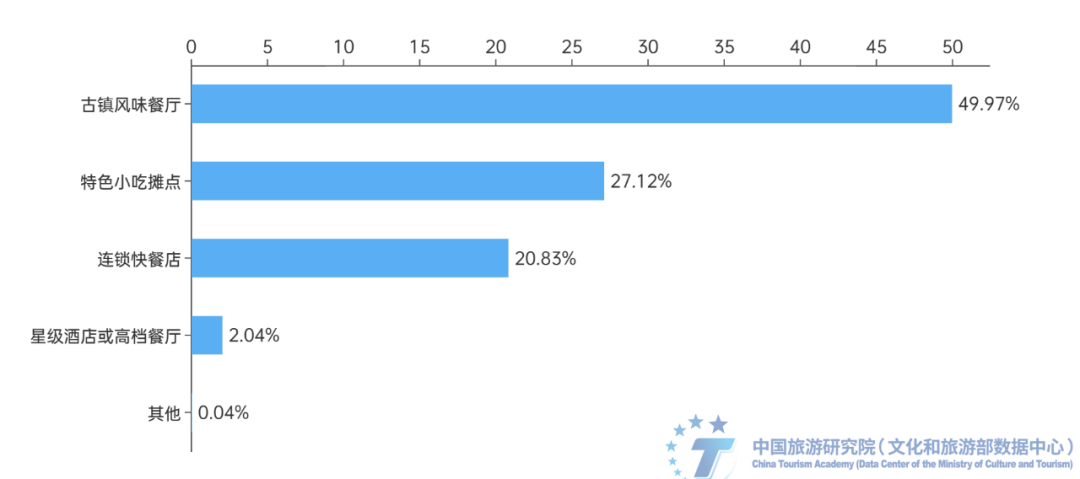
Figure 13 Proportion of respondents choosing different types of accommodation for ancient town tours
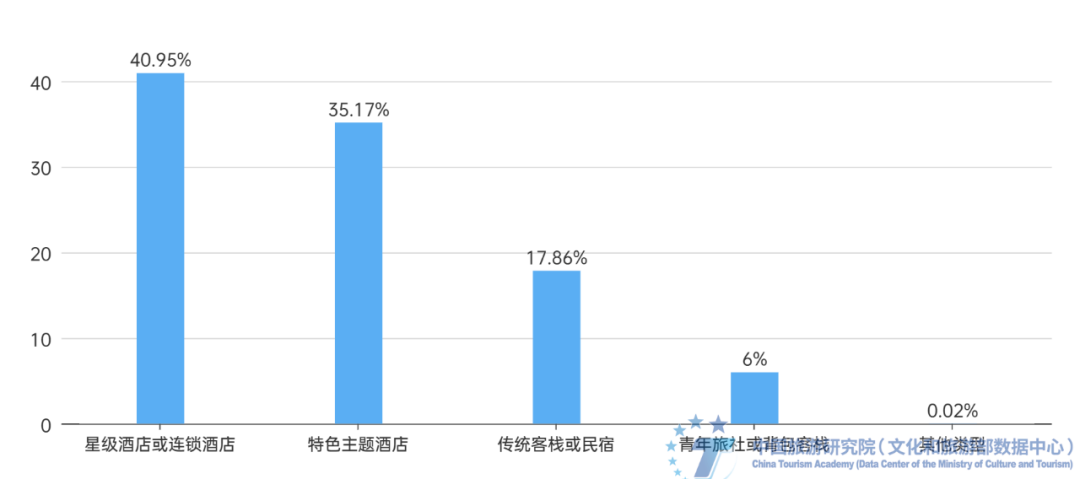
Figure 14 Reasons for choosing accommodation outside the ancient town and corresponding proportion of respondents
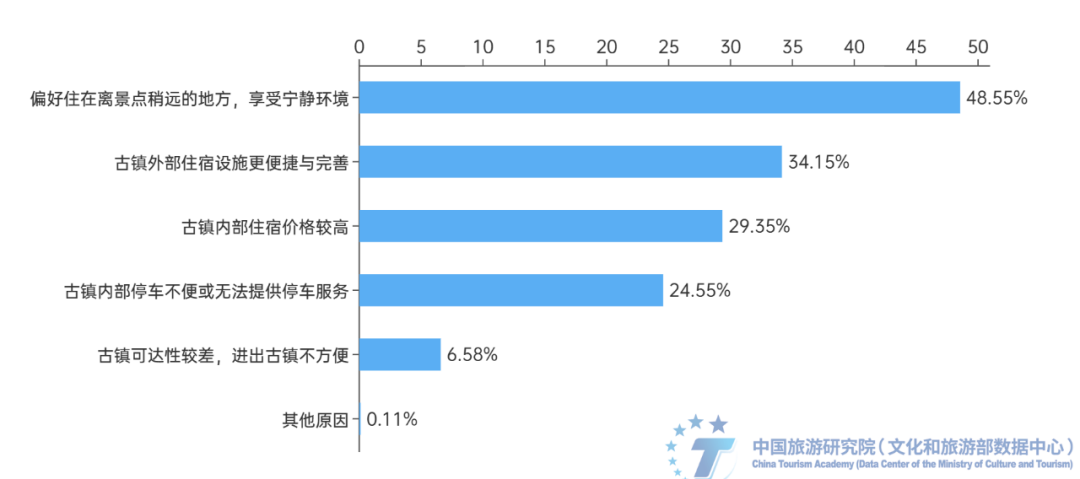
Figure 15: The range of accommodation prices that respondents consider suitable for tourism in ancient towns and the corresponding proportion of respondents
(6) Folk cultural activities provide a host guest interactive lever for the tourism space of ancient towns. Folk cultural activities in ancient towns are an important carrier for the integration of culture and tourism. The ancient town provides a space for tourists to engage in activities, while folk activities, dances, and music within the town offer the possibility of personal emotional stimulation and resonance for tourists. The survey shows that 92.77% of respondents are willing to participate in local folk activities, among which traditional festival celebrations are the most popular ancient town folk activities, accounting for 51.54%. Next is folk dance or music performance, accounting for 40.8%. Traditional handicraft experiences and characteristic folk games account for 22.37% and 26.19% respectively. In addition, more than half of the respondents think that the participation in folk activities in ancient towns is good or very good. There are certain activities for tourists to participate in, with rich and diverse activities and high tourist participation.
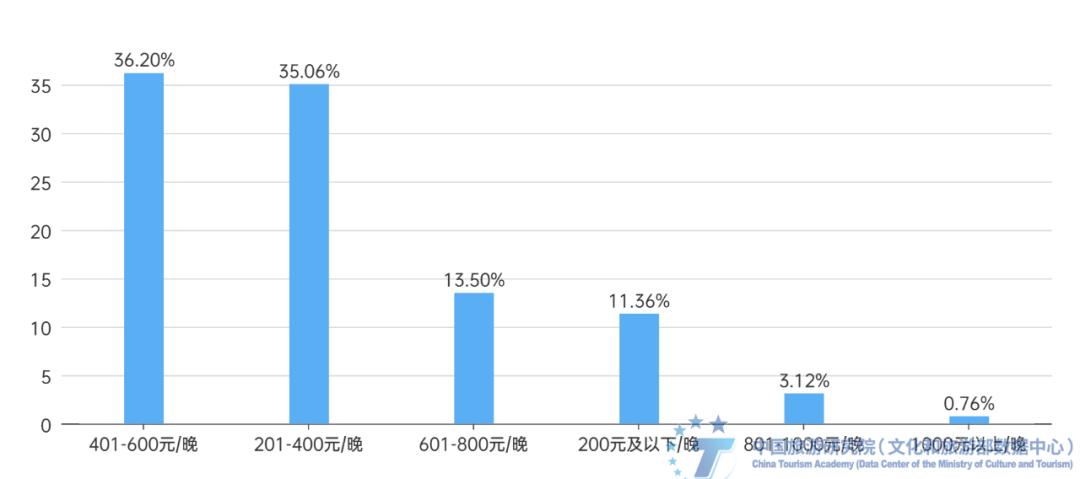
Figure 16: Folk activities in ancient towns that respondents participate in or expect to participate in
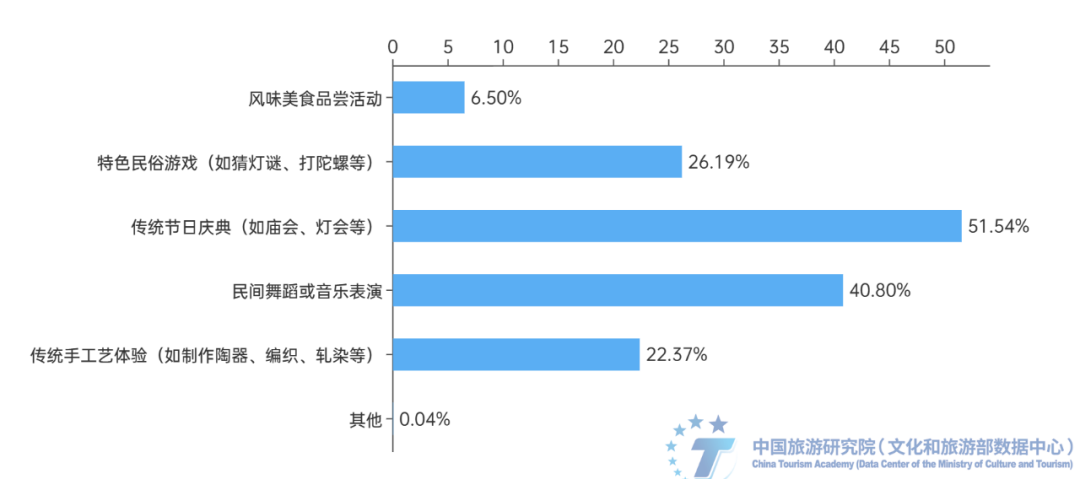
Figure 17 Participation in Folk Activities in Ancient Towns
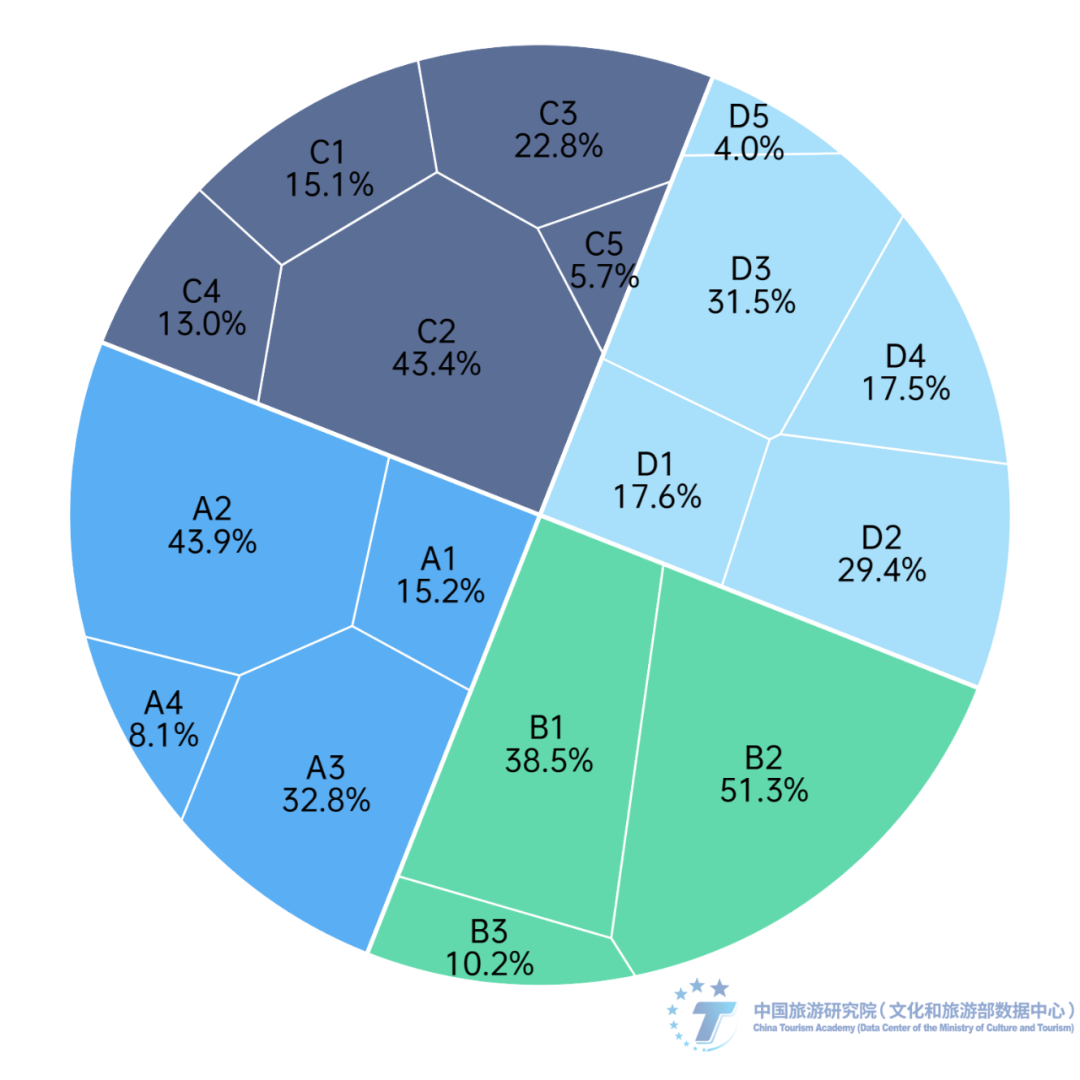
(7) The characteristics, types, and quality of tourism products affect tourists' willingness to purchase. Retail tourism products are high-frequency elements in tourism consumption, and their characteristics, types, and quality affect tourists' willingness to purchase. According to the survey, 62.82% of respondents sometimes purchase local specialties, and about 30.65% of respondents always like to buy local specialties as souvenirs or gifts for family and friends. At the same time, among the types of tourism products in ancient towns, handicrafts are the most popular, accounting for 27.58%, followed by antique art, accounting for 24.19%, and ranked third is ethnic clothing or accessories, accounting for 22.37%. Tourists in ancient towns tend to purchase products with local characteristics and cultural traditions, which can better showcase the local cultural charm and attract tourists' interest. In contrast, the selection rate of souvenirs is relatively low, accounting for only 2.16%, and further efforts are needed to enhance their attractiveness and uniqueness. Regarding the problems with tourism products in ancient towns, 42.50% of respondents believed that they lacked uniqueness and were similar to products from other places. 25.05% believed that the variety was single and the selection range was limited. 18.26% believed that the quality was poor, not durable, or easily damaged. This indicates that there is still significant room for improvement in the characteristics, types, and quality of tourism products in ancient towns. 4、 The problems and development directions of ancient town tourism: (1) The phenomenon of product homogenization, excessive commercialization, and short-term benefits has begun to emerge. Due to insufficient theoretical guidance, shallow innovation, and superficial imitation, in recent years, ancient town tourism has experienced product homogenization, excessive commercialization, short-term benefits, and non benign phenomena. According to a special survey conducted by the research group, 51.3% of the respondents believe that there are some similarities between ancient towns, and 38.5% of the respondents feel that ancient towns are very similar but lack uniqueness. The excessive commercialization, loss of authenticity, and low service quality of ancient towns have become the most concerning issues for tourists during their tourism journey; The lack of uniqueness in shops and products, as well as similarities in catering, are the main manifestations that respondents believe are similar in ancient towns. Data shows that nearly 60% of respondents believe that the loss of indigenous residents and lack of innovation are the main reasons for the homogenization of ancient town tourism (Figure 18).
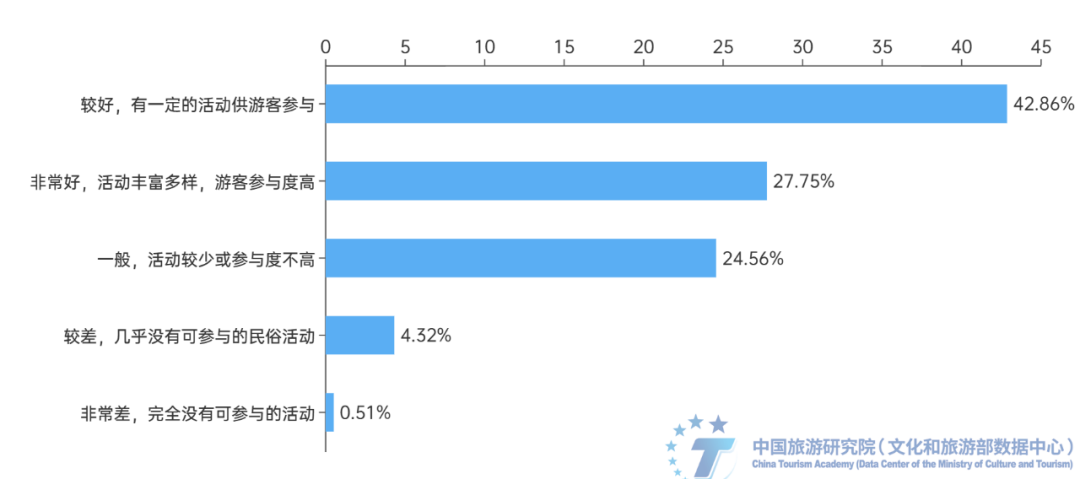
Figure 18 Survey results on the related problems faced by the development of ancient town tourism
Note: A represents the most concerning issue for respondents in ancient town tourism; B represents the interviewee's perception of whether there are significant similarities between ancient towns; C represents the respondents' belief that the main manifestation of homogenization in ancient towns; D represents the reason why the respondents believe that the ancient town is homogeneous. A1 represents crowded crowds; A2 represents excessive commercialization and loss of authenticity; A3 represents poor service quality; A4 represents poorly protected ancient towns with dirty and chaotic environments. B1 represents the feeling that many ancient towns are very similar; B2 represents some similarities; B3 represents dissimilarity. C1 represents similar architectural styles but lacks distinctive features; C2 represents a lack of uniqueness in the store and the products sold, mostly consisting of souvenirs and antique crafts; C3 represents that the catering in the ancient town is similar, lacking authentic local specialty cuisine; C4 represents cultural activities and experiential projects with similar content; C5 represents the same tourism service and management model. D1 represents the pursuit of rapid commercialization and tourism development; D2 represents the loss of indigenous people; D3 represents successful imitation cases, lacking innovation; D4 represents a lack of in-depth cultural exploration and inheritance; D5 represents insufficient government planning and policy guidance.
(2) The deep integration of culture and tourism to inherit the history of ancient towns and deepen the cultural experience of tourists is the key to achieving differentiated development and breaking away from homogenization in ancient town tourism. Ancient towns not only need to 'review history', but also need to 'innovate and move forward'. We should continue to invest in carefully crafted products, meticulous services, engaging activities, and efficient and optimized operations to ensure that the ancient town remains fresh and up-to-date. Taking the Wuzhen Drama Festival as an example, each edition presents different plays, and this continuous innovation and change have become the aspiration of countless tourists.
The uniqueness of ancient town tourism lies in the deep exploration of local culture, history, and tourism resources, providing tourists with immersive experiences, personalized tastes, and differentiated needs to meet. While maintaining the endogenous cultural heritage of the ancient town, it is also necessary to innovate the form of tourism products and promote the balanced development of the town's living, commercial, and tourism functions. By deeply integrating culture and tourism with high-quality development, we aim to promote innovation and industrial upgrading in the tourism industry of ancient towns.
The protection and development of ancient towns cannot be separated from local residents. Residents are not only an important component of the historical and cultural heritage of ancient towns, but also an intuitive window to showcase the unique styles and customs of each town. The key to making the historical and cultural protection and development of ancient towns have lasting vitality lies in retaining the indigenous people and their traditional way of life.
(3) The development and creation of ancient town tourism in the future, shaped by traditional culture, fashion elements, and modern services, requires the integration of traditional culture, fashion elements, and modern services to meet the dual requirements of tourists for historical and cultural experience and modern convenience facilities.
Exploring and showcasing the historical and cultural significance of ancient towns is the foundation for shaping tourism in these towns. The integration of fashion elements can add new vitality to ancient town tourism. On the premise of not destroying the original style of the ancient town, modern art design concepts can be introduced to create unique cultural and creative products and cultural activities, attract young tourists, and enhance the fashionable atmosphere of the ancient town.
Modern services are the key to improving the quality of ancient town tourism. A comprehensive infrastructure, such as convenient transportation, clean sanitation facilities, clear navigation systems, high-quality accommodation facilities, diverse catering services, etc., are all basic needs of tourists. The development of ancient town tourism should also pay attention to maintaining a balance between traditional culture and modern elements. Excessive commercialization can destroy the original charm of ancient towns, while being too traditional may cause inconvenience to tourists. Therefore, the development of ancient town tourism needs to cleverly integrate fashion elements and modern services while protecting traditional culture, creating a tourist destination that is both ancient and vibrant.
Exploring the traditional cultural heritage, integrating fashion elements, providing modern and convenient services, and creating an ancient town that combines historical and cultural charm with modern tourism experience will be an important path to attract more tourists to experience the unique charm of the ancient town.
Contribution | Edited by Planning and Leisure Institute | Source by Liu Xin | Reproduction by China Tourism Research Institute (Data Center of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism) Please indicate the author and source